Written by Robyn-Leigh van Laren in collaboration with ROEST Coffee

Every step that coffee takes in the process from seed to cup impacts its quality. Ensuring coffee quality at every touch point has been a steep learning curve for the Long Miles Coffee team, and is something they are continuously learning to improve with every coffee harvest that comes to pass.
“Could we actually produce specialty coffee in Burundi?“

When Long Miles’ co-founders, Ben and Kristy Carlson, moved to Burundi in 2011, they quickly realized that the most central place to see transformative change in the lives of coffee farmers and the quality of their coffee was at the washing station. In early 2013, the Carlsons built Bukeye, the first Long Miles Washing Station, with the underlying goal of answering the question, “Could we actually produce specialty coffee in Burundi?”
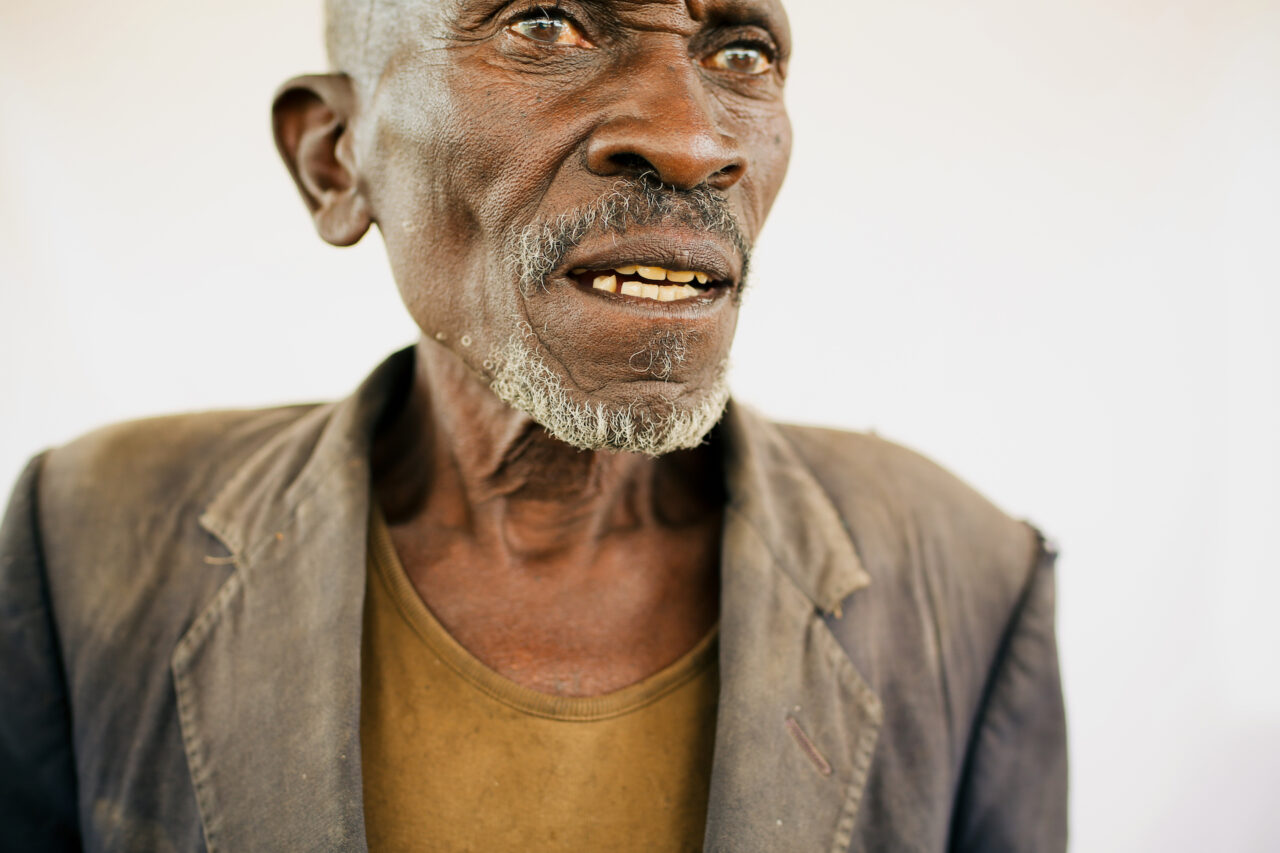
That same year, Lauren Kagori (née Rosenberg), a PhD candidate from South Africa, joined the Long Miles Team as their first Farmer Relations Officer. Kagori’s role was to understand coffee farmers’ relationship to the washing station. As they began to build trust and work with the coffee farming communities around the washing station, it became clear to Kagori that farmers’ greatest challenge to coffee quality was the lack of access to inputs: fertilizer, lime, mulch, and to some degree access to loans to pay laborers to work on their farms.
“You don’t just engage with farmers a month or two before harvest. It’s a year-round effort.”
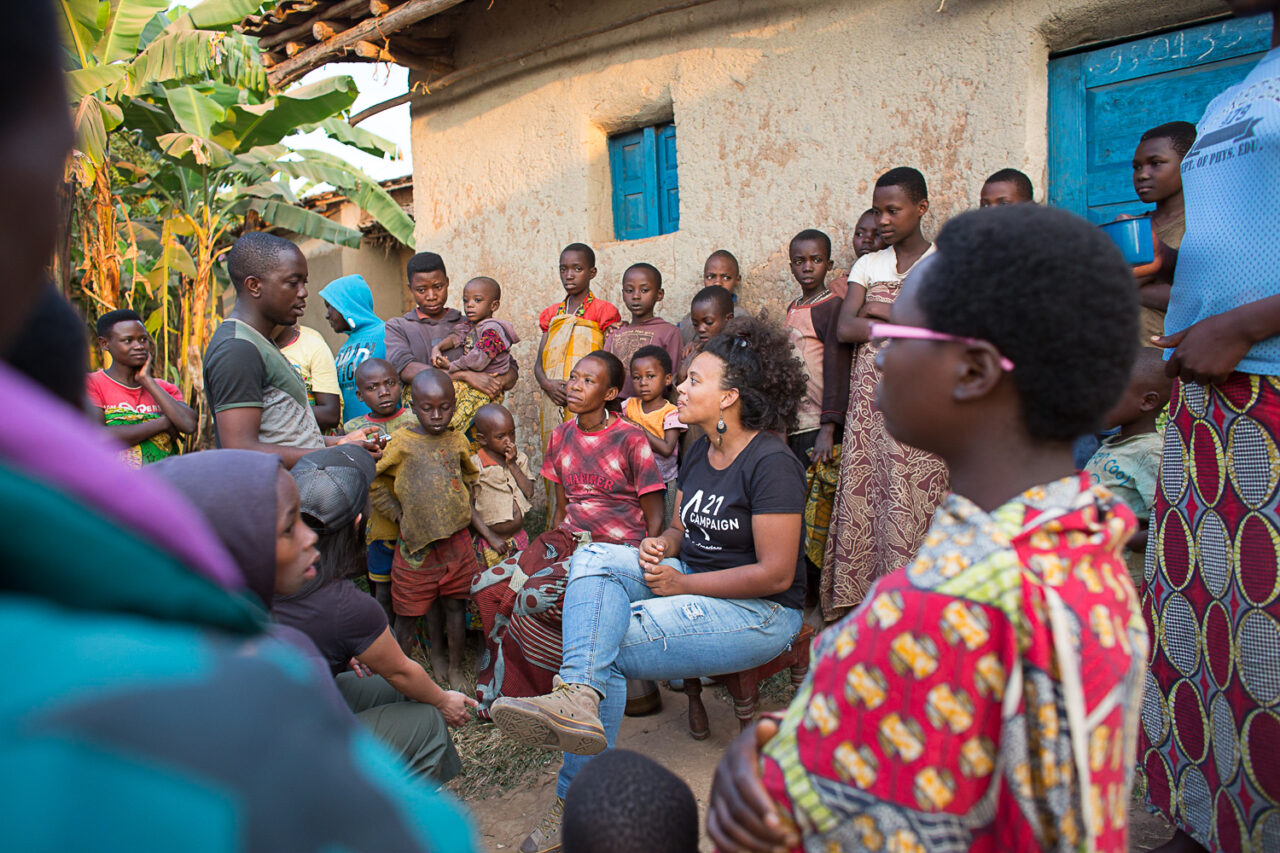
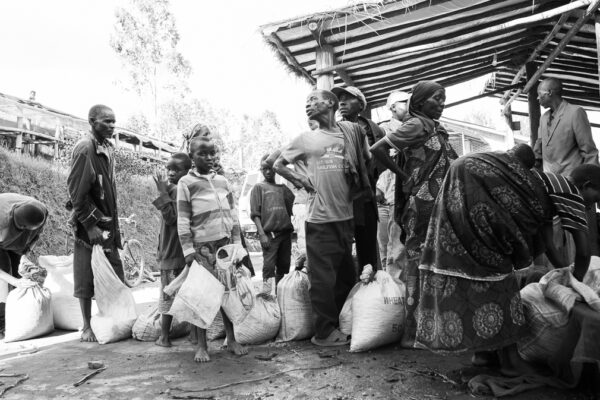
By the end of their first harvest, Long Miles produced only eighty bags of coffee- just a quarter of a container. Needless to say, the coffee didn’t taste very good that year and many roasters rejected the lots upon arrival in the United States. “We learned that you don’t just engage with farmers a month or two before harvest; it’s a year-round effort”, Kagori explains.
This was a turning point for Long Miles. They had built a washing station, invested in a community of smallholder coffee growers, and grown a team of people. But there was an obvious limit to the return on their investment if they didn’t invest in bottom lines that went beyond profitability.
Improving Coffee Quality on the Farm
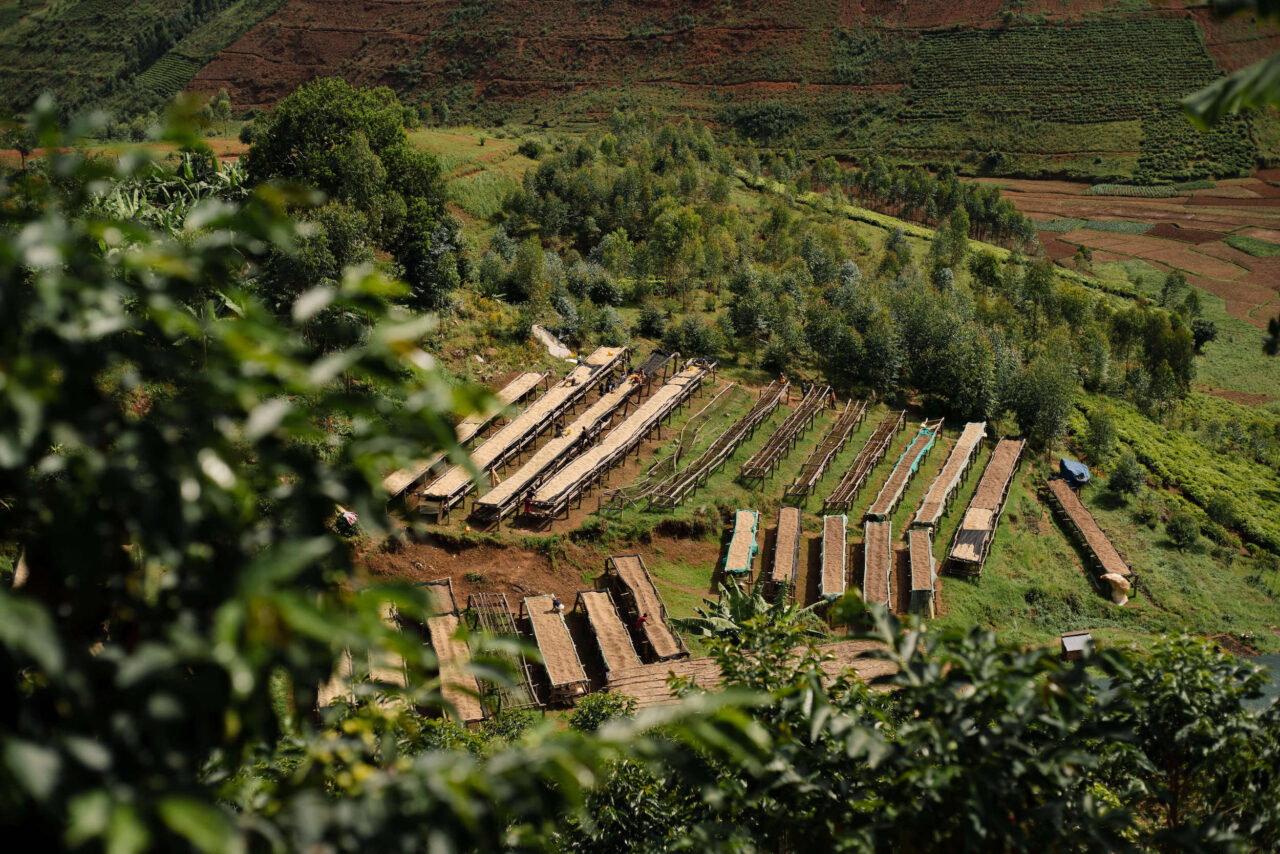
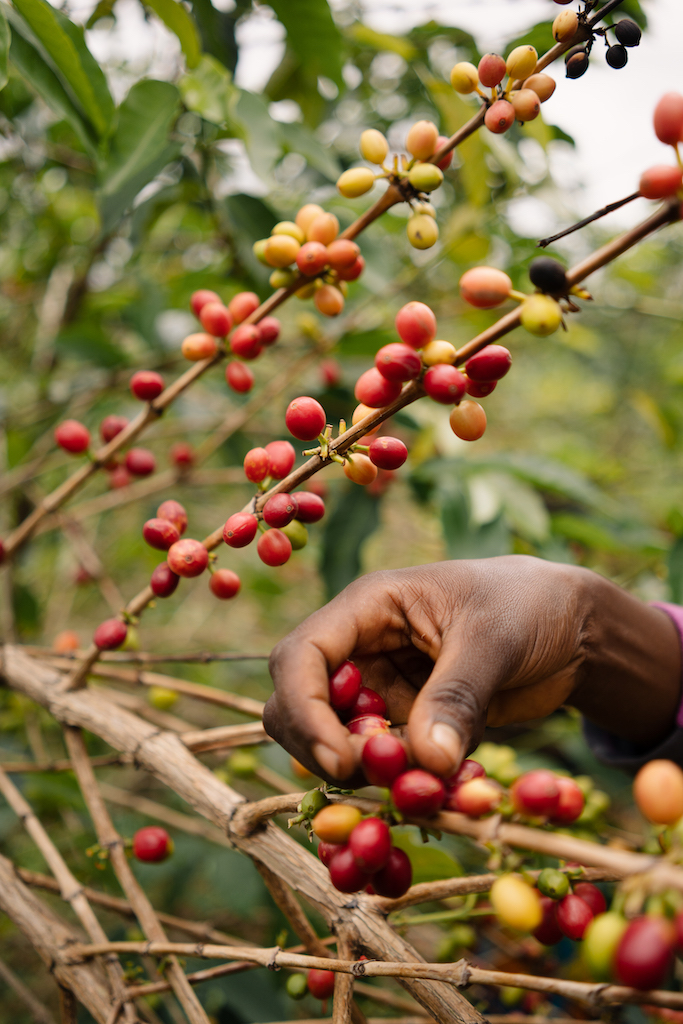
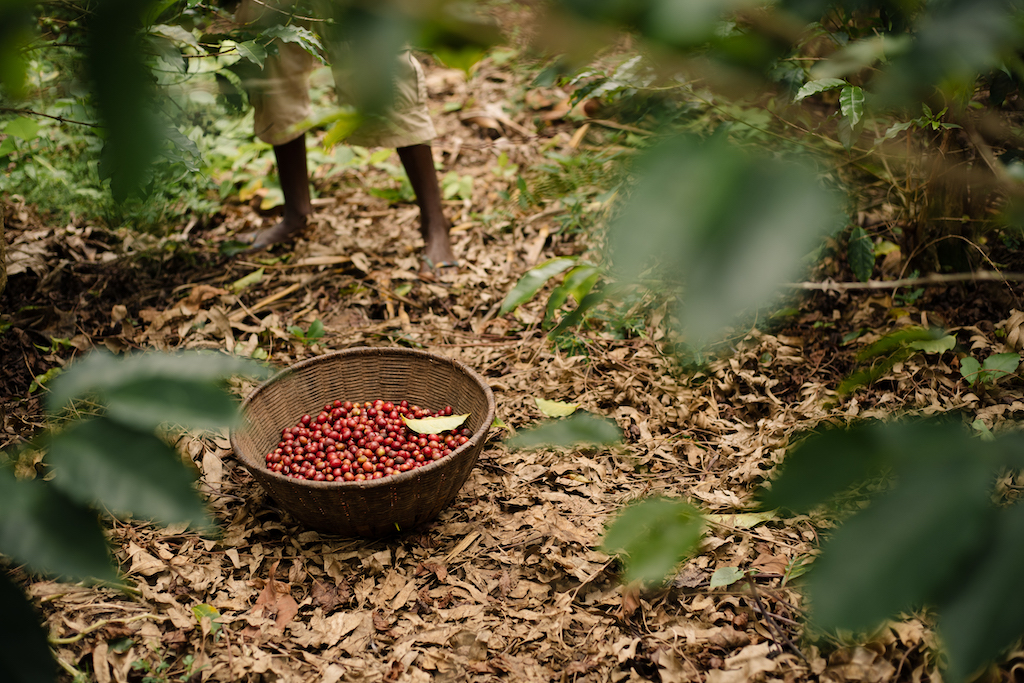
The Long Miles team came up with all sorts of innovative ideas to help guide farmers on how to improve their coffee’s quality. The first set of interns spent hours perusing local paint stores for the exact shade of red that resembled a ripened coffee cherry. The idea was to paint the bases of woven baskets that farmers generally use to collect hand-picked coffee cherries. It quickly went from baskets to dipping small wooden chips in the same red paint that farmers could easily slip in and out of their pockets to compare their ripening cherries against. Back at the washing station, a borehole was drilled so that their team could start processing coffee with clean groundwater instead of water from a nearby river.
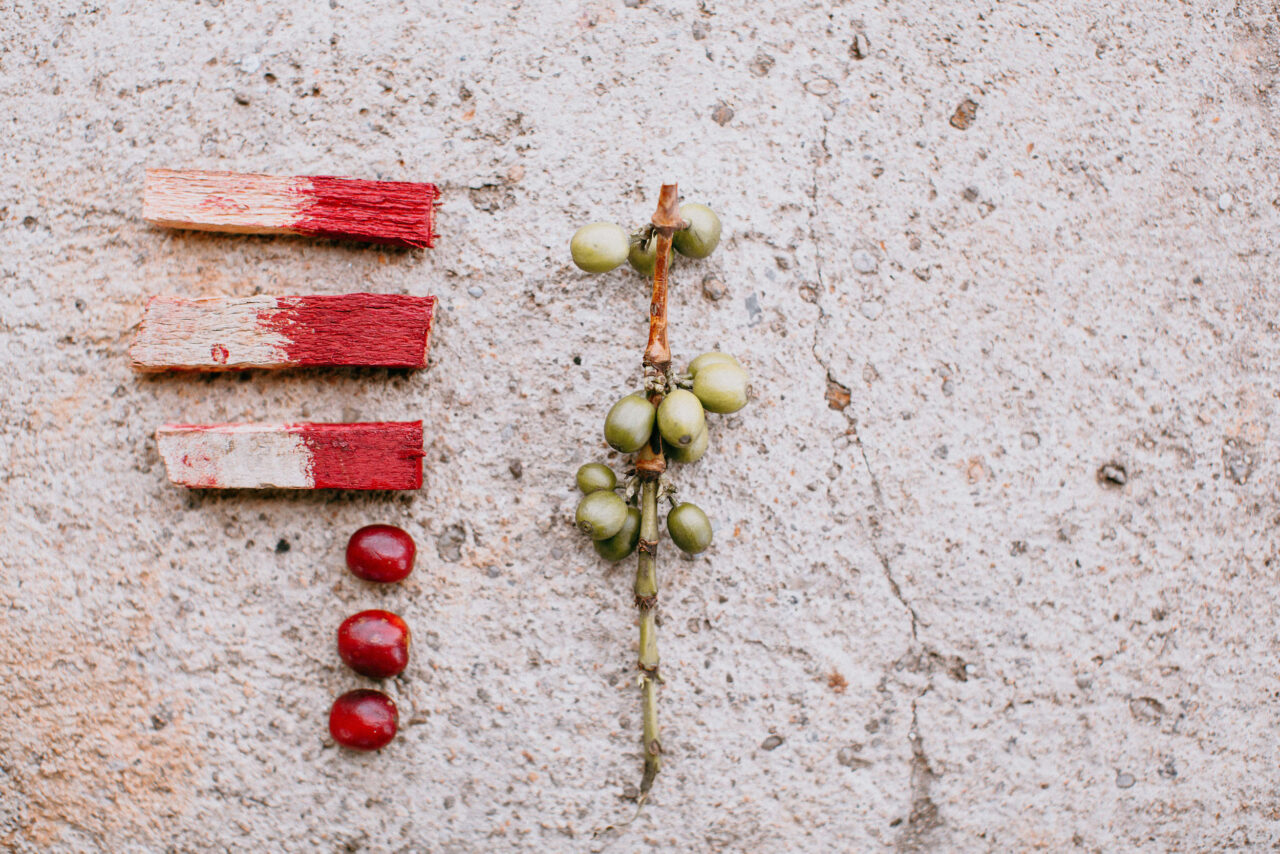

Around that time, another challenge was rising, both at the farm level and on the cupping table: the Potato Taste Defect. It took a trip to visit an established coffee producer in Rwanda and interviews with Long Miles’ partner roasters to realize that Potato Taste Defect was a real issue- not just in Burundi, but in neighboring coffee-growing countries too. That’s how the Long Miles Coffee Scouts came to be.
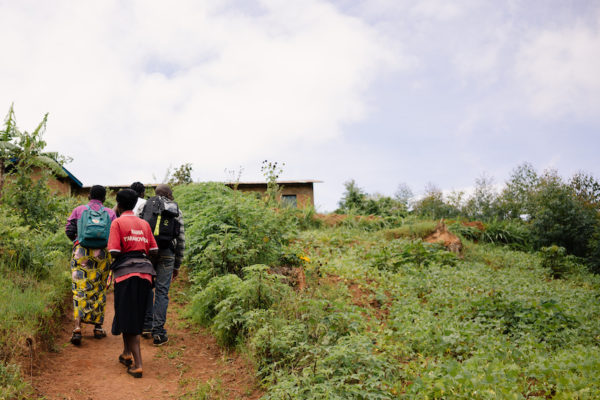
Led by Epaphras Ndikumana, Social and Environmental Impact Leader at Long Miles, the Coffee Scouts guide partner farmers through the cherry picking process on their farms while also scouting for and removing any antestia bugs (the insect linked to the Potato Taste Defect). The Coffee Scouts also encourage farmers to practice floating cherries at home and then again at the washing stations. Standing side-by-side with farmers at the washing stations, the Scouts help to hand-sort their cherries for ripeness and visible defects. Back on the farm, they distribute indigenous and shade trees to partner coffee farmers, encouraging them to plant green manures to improve soil health, mitigate climate change and the productivity of their coffee trees. The Coffee Scouts have been pivotal in improving the quality of Burundi coffee, and the Potato Taste Defect has since become increasingly less common on our cupping tables.
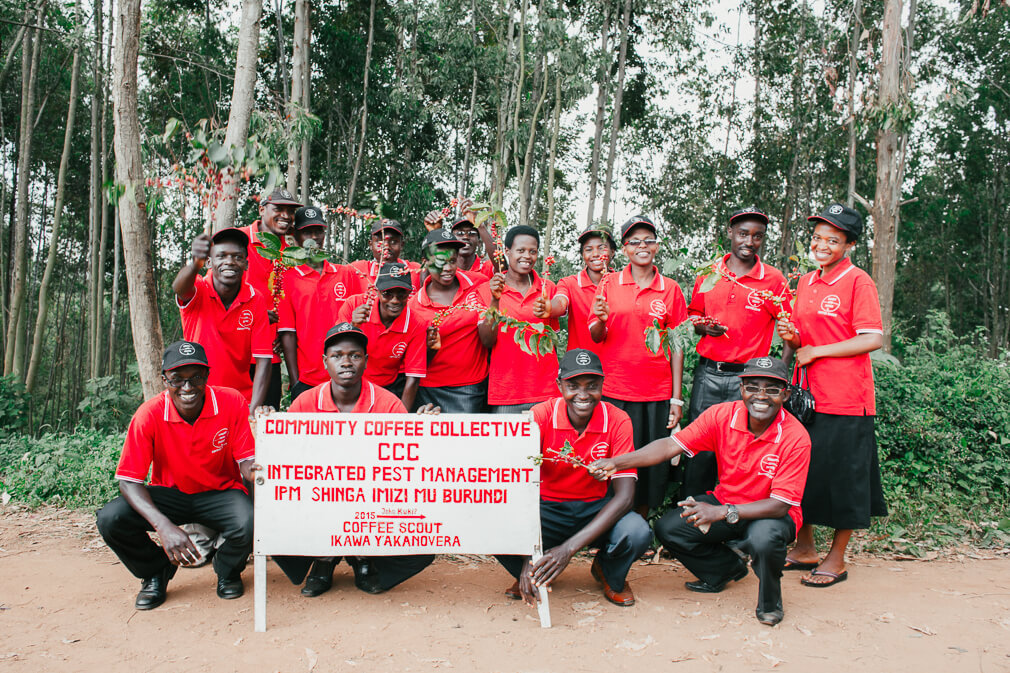

“The activities of our social projects help partner coffee farmers to improve their agricultural practices which increases the productivity and quality of their coffee in the long run”, Ndikumana says. He has done extensive research on how to improve the productivity of Burundian farmers’ coffee trees and soil health, initiating programs like the PIP approach (translated from French as ‘Integrated Farm Plans’) and Farmer Field Schools within the farming communities that Long Miles works with in Burundi.
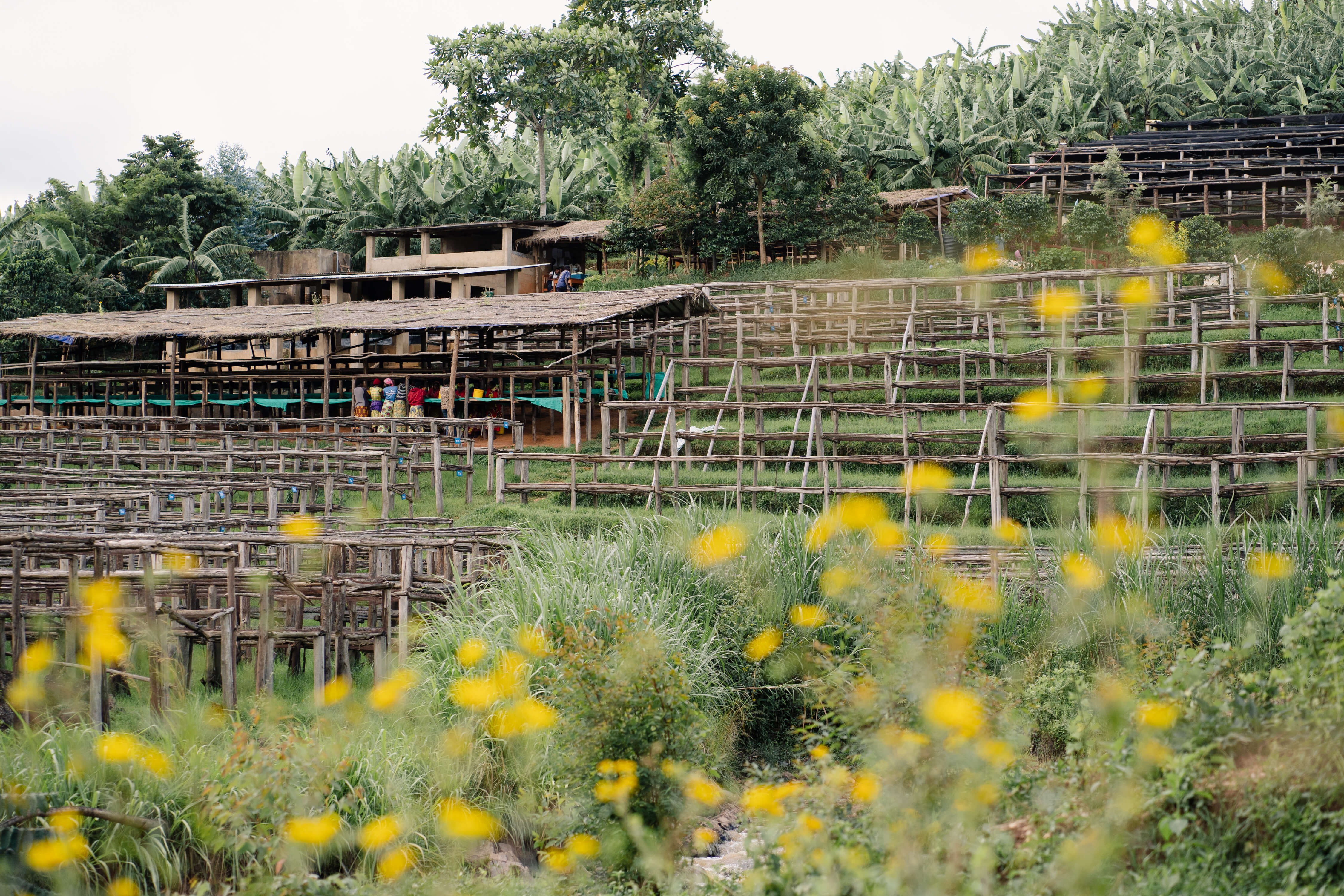
Long Miles’ Coffee and Quality Production Manager, Seth Nduwayo, adds to this by explaining that, “Our protocols, standards and communication are the most powerful tools that help us to produce quality coffee in a systemized way. We don’t only make efforts to perform well but try to make sure we perform more consistently while also aiming to improve our performance.” Ensuring coffee quality quietly continues long after harvest has ended at the dry mill. Nduwayo and the Long Miles team spend weeks at a time, following their coffee through innumerable quality steps at the mill: from hulling to grading, density sorting, handsorting, weighing, and eventually loading containers for export.
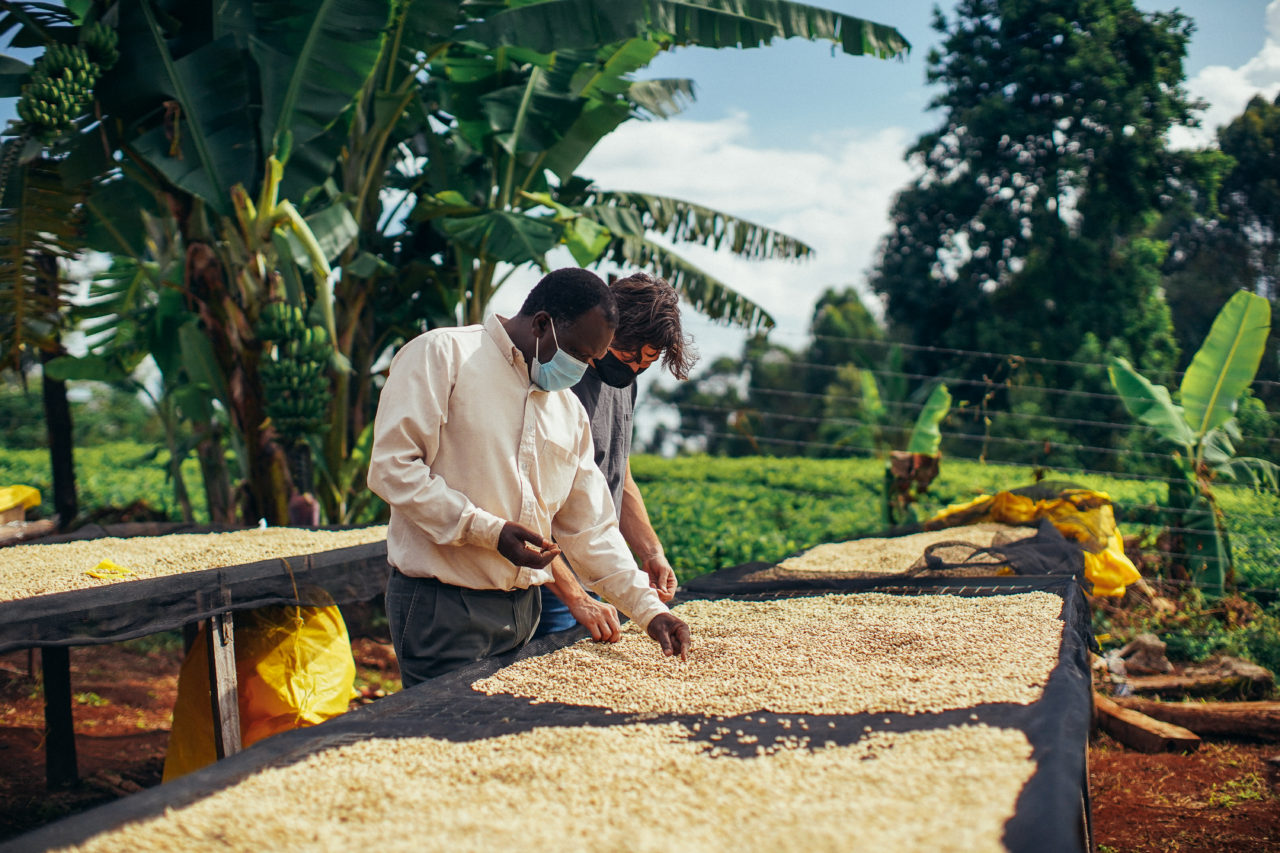
Green grading and sample roasting
On the other side of the world, David Stallings, head of Roaster and Importer Relations, ensures that coffee goes through meticulous quality steps once it reaches the Long Miles Coffee Lab in North America. He starts by measuring the water activity, performing a moisture and UV analysis of the coffee weighing and then roasting each sample using our ROEST. All the relevant physical data about each sample is documented before the process is repeated over and over again before samples are sent to their roasting partners across the globe.
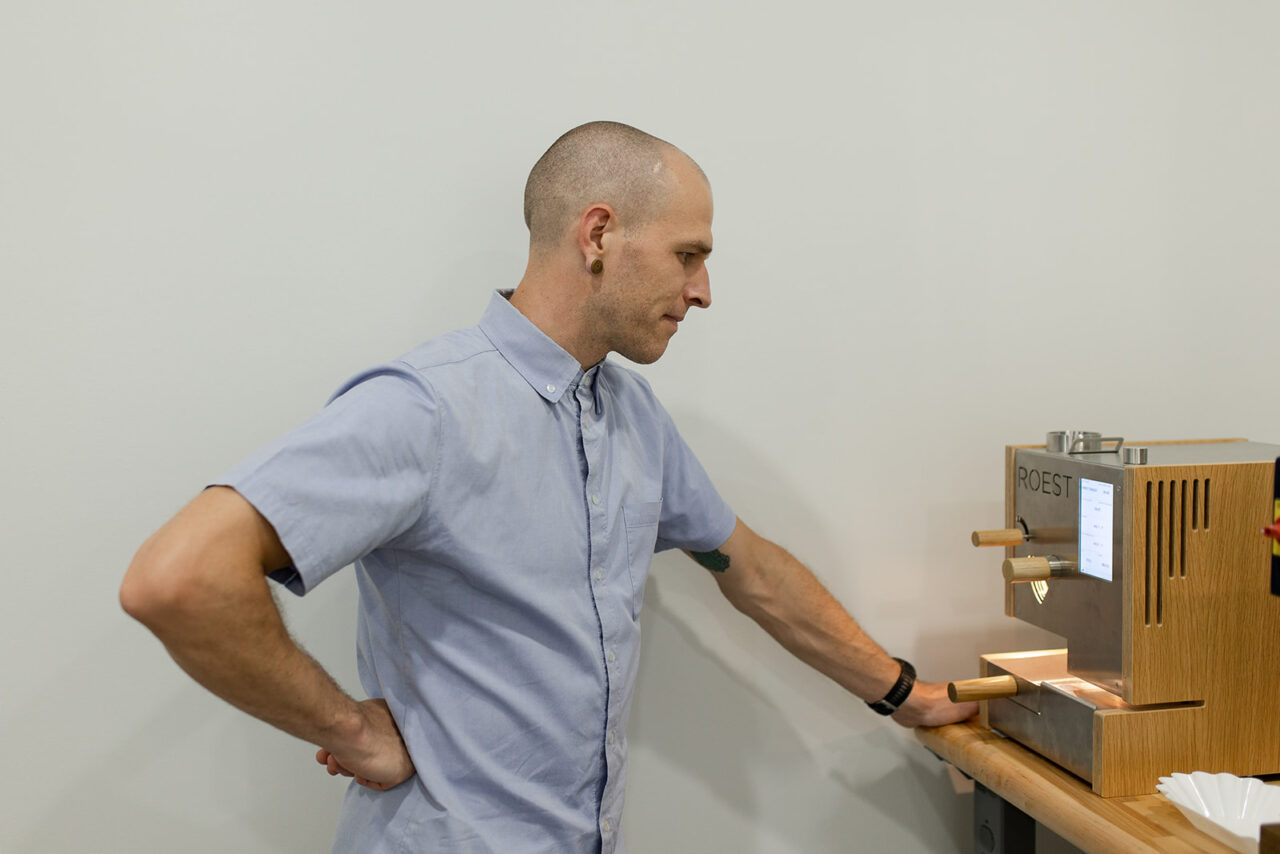

During coffee season, Stallings typically processes and on ROEST around 120 samples a week:
“The ROEST sample roaster may be the most perfect small-scale machine yet designed to explore the many different aspects of coffee roasting that I learned about through various roasting systems. The capability to develop profiles based on different parameters and the machine’s ability to develop coffee remarkably evenly, coupled with its ease of use and maintenance, make it an essential tool in my professional life.”
Click below to read more about how David Stallings developed the Long Miles ROEST profiles.
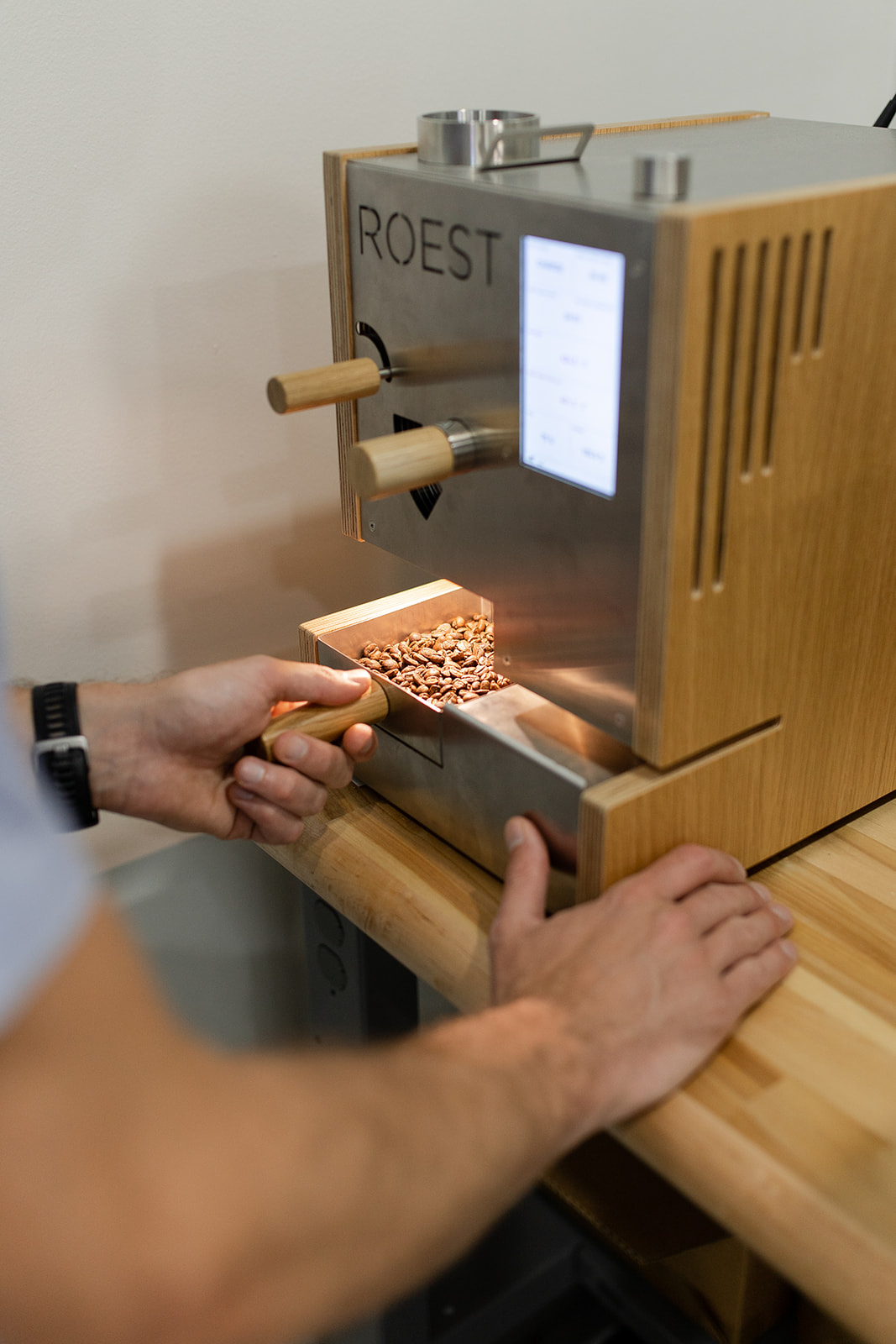

Coffee Quality is about People.
It would be remiss not to acknowledge that there is countless research, processes, and tools, like the ROEST sample roaster, used at every touchpoint along coffee’s journey, but ensuring the quality of Long Miles’ coffee really comes down to people. Each coffee farming family that Long Miles works with. By continuing to listen to their thoughts and understand their challenges and needs, they continue to put steps in place to improve the quality of their coffee. The team of Coffee Scouts, working tirelessly throughout the year guiding partner farmers on best agricultural practices. It’s every member of the Long Miles team, investing in the long-term impact of smallholder coffee farmers in East Africa and the coffee they produce.
All this before any coffee reaches your cup.

































